The understanding of the molecular and cellular basis of aging has grown exponentially over recent years
, and it is now accepted within the scientific community that aging is a malleable process; just as it can be accelerated, it can also be slowed and even reversed.
1. Supplement-Based NAD+ Therapy (The Most Common Form)
This involves oral or sublingual intake of NAD+ precursors—compounds the body uses to make NAD+. This is the foundation of most consumer and wellness-focused "NAD+ therapy."
Common Precursors:
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR): Sold as brands like Tru Niagen. Backed by significant human clinical trials showing it safely raises NAD+ levels and may improve markers of cardiovascular and metabolic health.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN): Widely available as a supplement. Extremely effective in mice, but human data is still emerging. Its legal status as a supplement in the US has been challenged by the FDA.
Nicotinamide (Nam) & Niacin (NA): Forms of Vitamin B3. Effective but have limitations (niacin causes flushing; nicotinamide can inhibit sirtuins at high doses).
Mechanism: These compounds bypass rate-limiting steps in NAD+ biosynthesis, allowing cells, especially in key organs like the liver, brain, and muscle, to replenish their declining NAD+ pools.
Goal: Slow cellular aging, boost mitochondrial function, enhance DNA repair, and support metabolism by activating sirtuins (SIRT1, SIRT3) and other NAD+-dependent enzymes.
---
2. Intravenous (IV) NAD+ Therapy (An Emerging Clinical Procedure)
This is a more direct, intensive, and medicalized approach where bio-identical NAD+ is administered intravenously.
The Procedure: A slow IV drip, often over 2-4 hours, delivering NAD+ directly into the bloodstream. Sessions may be repeated over several days (a "protocol").
Proposed Rationale: Bypasses the gut entirely, achieving potentially higher cellular concentrations in target tissues without digestion or first-pass liver metabolism.
Claimed Uses (Anecdotal & Clinical):
Rapid detoxification & addiction recovery (for alcohol, opioids, stimulants) – this is its most established, though still off-label, use. The theory is that it helps "reset" brain chemistry and repair neuronal damage.
Severe chronic fatigue (e.g., from Long COVID, ME/CFS)
Acute cognitive enhancement & "brain fog" relief
Neurodegenerative conditions (Parkinson's, Alzheimer's - very experimental)
Anti-aging "rejuvenation"
Important Caveats for IV Therapy:
Limited Robust Evidence: While compelling anecdotes and some small clinical reports exist, large-scale, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are lacking compared to oral precursors like NR.
Cost & Accessibility: Very expensive (hundreds to thousands of dollars per protocol), typically offered at specialized functional medicine or wellness clinics.
Side Effects: Can cause chest tightness, anxiety, nausea, and fatigue during the infusion (likely due to rapid cellular activation). Must be administered by a medical professional.
Regulation: It's an off-label use of a molecule, not an FDA-approved treatment for any specific disease.
3. The Core Idea Behind Any NAD+ Therapy: Address the "NAD+ Decline"
All forms operate on the same scientific premise illustrated below:
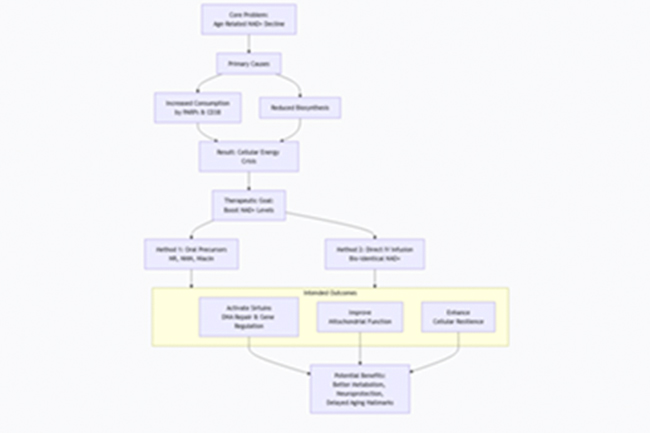
Current Medical & Scientific Consensus
1. The Science is Solid: The biology of NAD+ and its decline with age/stress is well-established in peer-reviewed literature.
2. Oral Precursors are Proven to Raise NAD+: NR and NMN have been shown in multiple human studies to significantly increase blood NAD+ levels. Evidence for functional benefits (e.g., improved arterial flexibility, insulin sensitivity) is promising and growing.
3. IV NAD+ is More Speculative: It represents a more aggressive intervention. While mechanistically plausible and reported to be effective for certain conditions (like addiction in clinical settings), it lacks the same volume of rigorous long-term human data as oral precursors. It is considered experimental for most indications.
4. Not a Magic Bullet: NAD+ therapy is best viewed as a powerful supportive intervention within a holistic framework of good nutrition, exercise, and sleep. It addresses a fundamental metabolic deficiency but is not a cure for complex diseases alone.
How to Approach NAD+ Therapy
For General Health & Prevention: High-quality oral NAD+ precursors (NR or NMN) are the evidence-based, safe, and accessible starting point.
For a Specific, Debilitating Condition: If considering IV NAD+, it is essential to:
Consult with a knowledgeable physician.
Inquire about the clinic's protocols, safety measures, and experience.

Dr. Med. Mahmoud Taghavi
Facharzt für Allgemeinmedizin
Facharzt für Arbeitsmedizin FMH
BAV-Offizierarzt
Taucherarzt (SUHMS / GTÜM)